The goal
The goal of the procedure is to have the ability of an individual or couple to start a family at a time of their choosing.
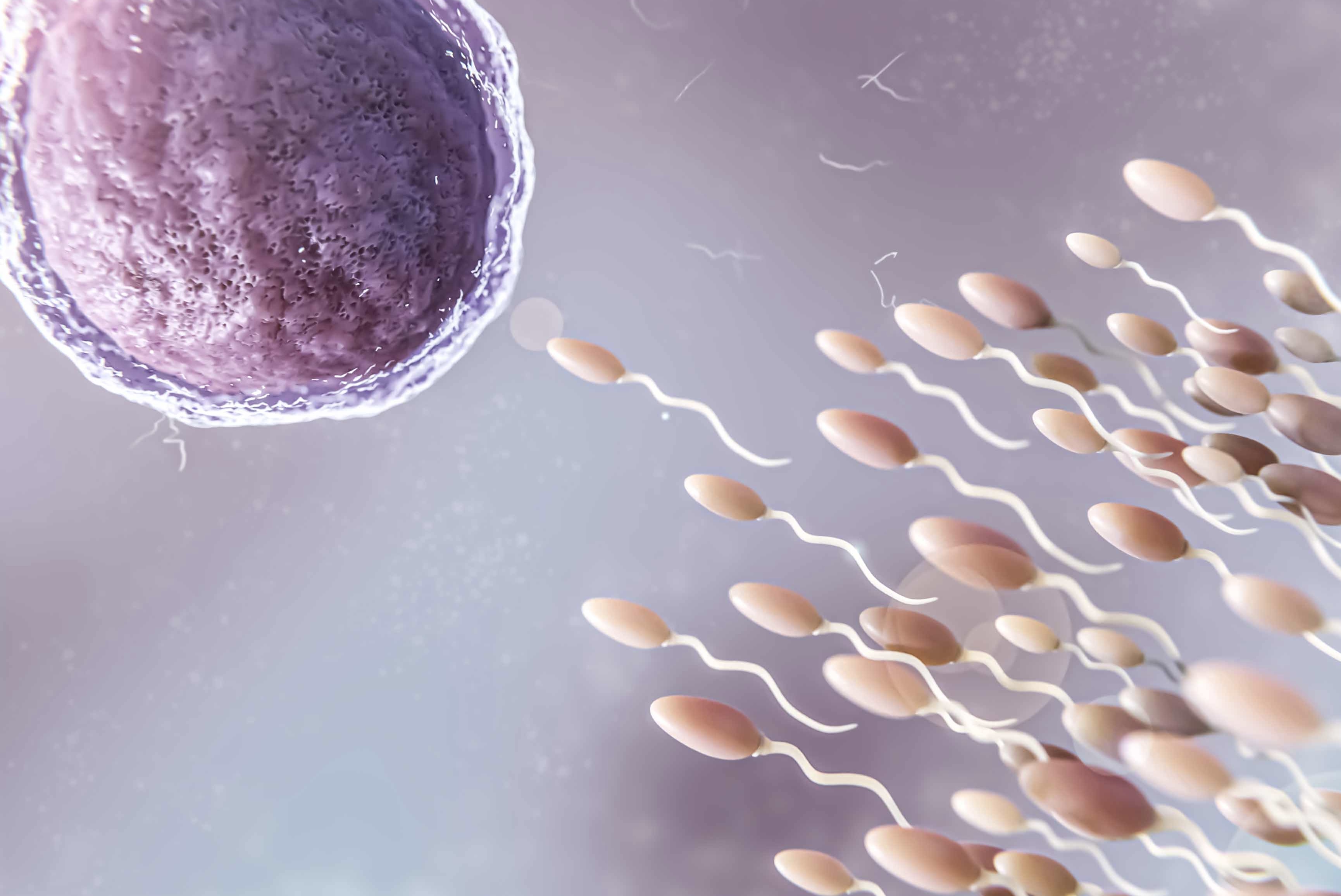
Egg freezing, or oocyte cryopreservation, is a medical procedure that empowers women to preserve their fertility by freezing and storing them at a younger age, when the eggs are typically of higher quality. This process is increasingly popular among women who wish to delay childbearing for various reasons, such as career planning, educational pursuits, or the absence of a suitable partner.
The Egg Freezing Process
- Pre-treatment Consultation and Testing:
Before the egg-freezing process begins, women undergo a thorough medical evaluation. This includes a pelvic exam, blood tests to assess hormone levels, and an ultrasound to examine the ovaries. These tests help determine the health of the woman’s ovaries and her potential response to fertility medications. - Ovarian Stimulation:
Similar to the initial stages of IVF, egg freezing involves stimulating the ovaries with hormonal injections that encourage the ovaries to produce multiple eggs during one menstrual cycle. This process usually lasts about 10 to 14 days. Throughout this period, the woman’s response to the medication is monitored through regular blood tests and ultrasound examinations to track the development of the follicles (where eggs mature). - Egg Retrieval:
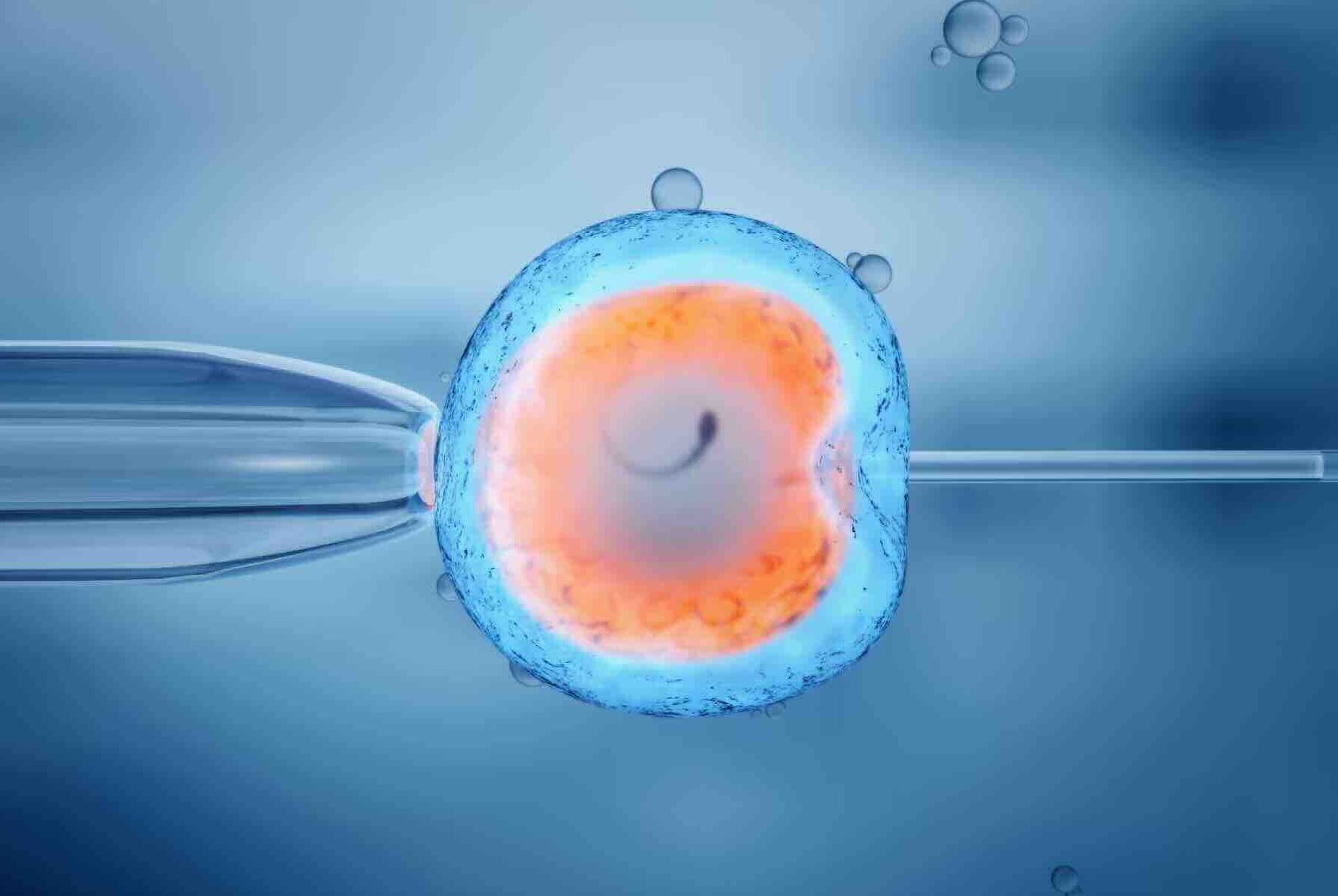
Once the eggs have matured, a retrieval procedure is scheduled. This is a minor surgical procedure performed under sedation or anesthesia. A thin needle is passed through the vaginal wall under ultrasound guidance to aspirate the eggs from the follicles. The entire process typically takes about 20 to 30 minutes. - Freezing:
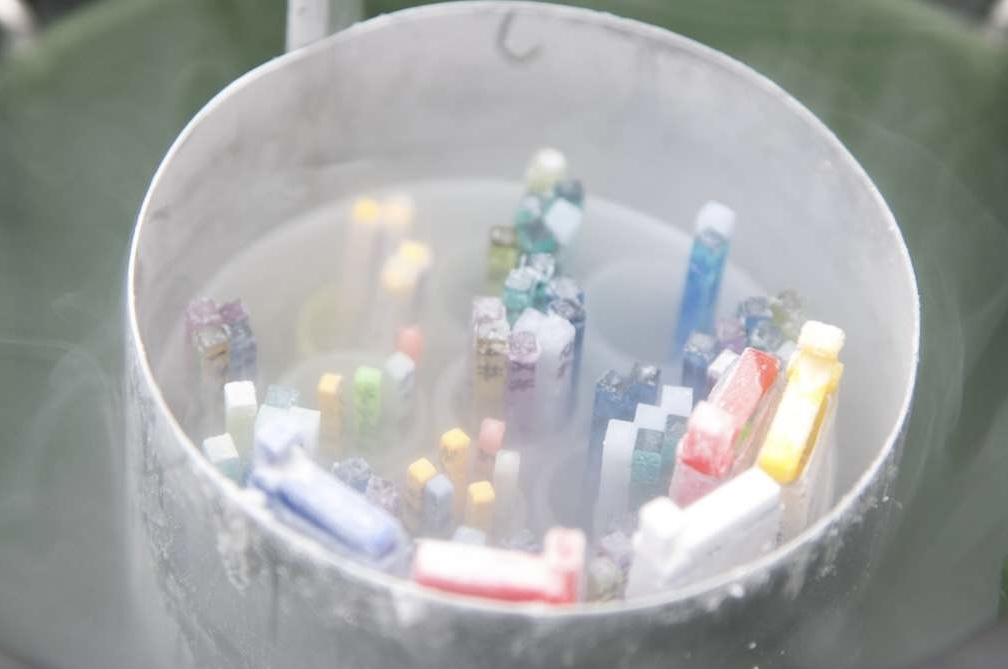
The retrieved eggs are then assessed in the lab to determine their viability. Healthy, mature eggs are frozen using a process called vitrification. Vitrification is a rapid freezing technique that minimizes ice crystal formation, which could damage the cell. The eggs are treated with a protective substance (cryoprotectant) before being flash-frozen and stored in liquid nitrogen tanks.
Reasons for Egg Freezing
- Medical Reasons:
Women diagnosed with medical conditions such as cancer that require treatments like chemotherapy or radiation, which can harm fertility, often choose to freeze their eggs before undergoing treatment. - Personal and Social Reasons:
Many women opt for egg freezing to delay pregnancy until a time that better fits their personal or professional life goals. - Risk of Diminished Ovarian Reserve:
Women at risk of premature ovarian aging due to genetic factors or other conditions may freeze their eggs to try to ensure future reproductive possibilities.
Considerations and Success Rates
The success of egg freezing largely depends on the age at which the eggs are frozen. Eggs frozen at a younger age are more likely to lead to a successful pregnancy later on. According to various studies and clinical data, the likelihood of achieving a live birth from frozen eggs decreases as a woman’s age at freezing increases.
The decision to freeze eggs is a significant one involving emotional, financial, and physical factors. The cost can be considerable, involving expenses for the procedure, medication, and long-term storage of the eggs.
Egg freezing is a powerful technology that offers women autonomy over their reproductive timeline, allowing them to preserve their fertility until they are ready to start a family. However, it is essential for women considering this option to consult with fertility specialists to understand the realistic outcomes and potential risks associated with the process.
If you have any questions about our fertility treatment plans, AFMC Care Team, or medical center, explore our website or message us at the Contact Us page!