Semen Analysis
A semen analysis is a diagnostic test commonly used to assess male fertility. It involves examining a semen sample to evaluate various parameters related to sperm health and function. These parameters typically include:
- Volume of ejaculate: This refers to the amount of semen produced during ejaculation. An average volume is typically between 1.5 to 6 milliliters.
- Sperm concentration (or density): This measures the number of sperm in a given semen volume. A higher concentration of sperm indicates better fertility potential. An average concentration is typically greater than 15 million sperm per milliliter.
- Sperm motility: This assesses the ability of sperm to move effectively through the female reproductive tract. Motile sperm are necessary to reach and fertilize the egg. Sperm motility is usually expressed as a percentage of sperm that exhibits progressive movement. A higher percentage of motile sperm is indicative of better fertility potential.
- Sperm morphology: This evaluates the shape and structure of sperm. Normal sperm morphology is essential for sperm to penetrate and fertilize the egg. Morphology is typically assessed based on the percentage of sperm with standard shape and structure. A higher percentage of normal-shaped sperm is associated with better fertility potential.
Overall, a semen analysis provides valuable information about sperm health and can help identify potential causes of male infertility. It is often one of the first steps in diagnosing male fertility issues and guiding appropriate treatment strategies.
Sperm Chromatin Structure Assay (SCSA)
The Sperm Chromatin Structure Assay (SCSA) is a diagnostic test used to detect abnormalities in sperm DNA. This test was first developed by Evenson in 1980.
During the SCSA, sperm samples are analyzed using flow cytometry. This method measures the susceptibility of sperm DNA to acid-induced denaturation, which means it determines how easily the DNA unwinds when exposed to acid.
If sperm DNA is abnormal and prone to fragmentation, it will show increased susceptibility to acid-induced denaturation during the SCSA. This indicates that the sperm has issues with its chromatin packaging, which can affect its ability to fertilize an egg.
In simple terms, the SCSA helps identify sperm with DNA damage, which may impact fertility and increase the risk of pregnancy complications.

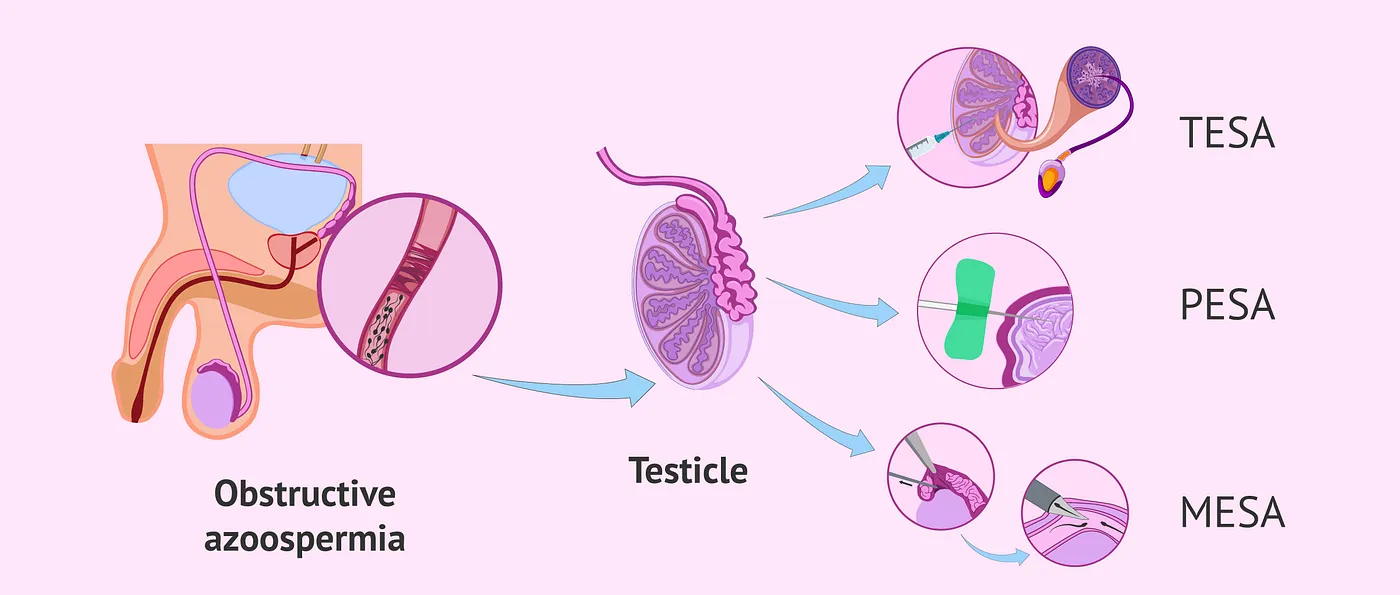
Tesa tese mesa pesa
PESA, TESA, and MESA are infertility treatments that involve surgically collecting sperm from the male partner’s testicles. These treatments are helpful for couples dealing with severe male infertility issues and are typically done under local anesthesia. The collected sperm can then be used for fertility treatments such as in vitro fertilization (IVF) or intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) to help the patients conceive a child.
PESA (Percutaneous Epididymal Sperm Aspiration) involves using a needle to collect sperm from the epididymis, a small tube where sperm are stored.
TESA (Testicular Sperm Aspiration) is similar, but the sperm is collected directly from the testicles using a needle.
MESA (Microsurgical Epididymal Sperm Aspiration) is a more intricate procedure that involves making a small incision in the scrotum to access the epididymis and collect sperm directly.
history and physical examination
At your initial fertility consultation, AFMC’s Male Infertility Specialists will carefully review your medical history and perform a simple physical examination. This helps us understand if factors such as lifestyle, medications, or genetic influences may affect fertility.

Hormone blood test - FSH, LH, E2 and Testosterone
Blood tests commonly performed to assess male fertility may include measuring levels of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), total testosterone, and estradiol (E2). These tests are instrumental in diagnosing potential causes of male infertility and guide treatment decisions.
Elevated FSH levels may indicate a problem with sperm production in the testes, while LH levels play a crucial role in regulating testosterone production.
Testosterone is essential for sperm production, significantly when low levels can impact fertility and a man’s overall health.
Estradiol (E2) levels provide valuable information about hormone balance, which can affect sperm production and overall reproductive health.